Entry 1: System Initialization & Line Detection
🚀 Initialization
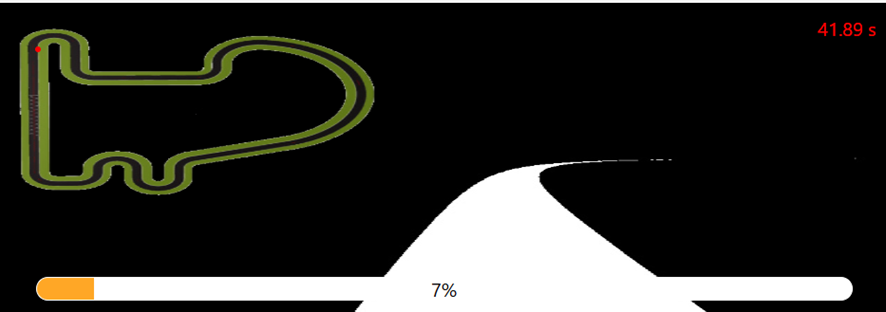
First, it is important to start with a simple and basic test to observe how the system works and to get familiar with the environment and the conditions in which we will be working. For this reason, I started the car in the Simple Circuit at a very low and constant linear speed, with no rotational speed.
The first observation is the image captured by the camera:
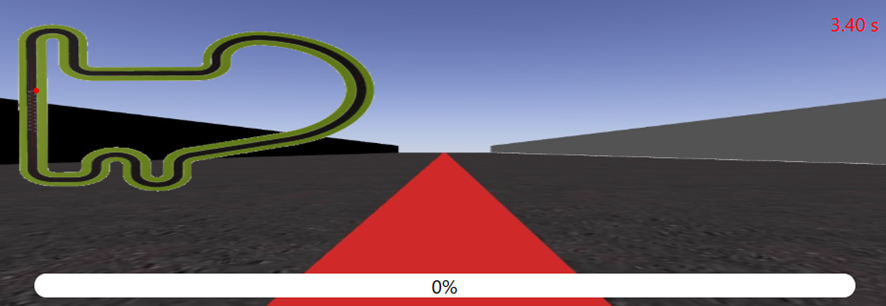
Since the rotational speed is 0 and constant, the car moves in a straight line and exits the track at the first curve.
🎯 Line Detection
The first step to guiding the car along the line is to detect the reference line. To achieve this, I printed the RGB value of the central pixel from the first iteration of the loop, which corresponds to a pixel in the line. The result obtained is [41, 41, 207].
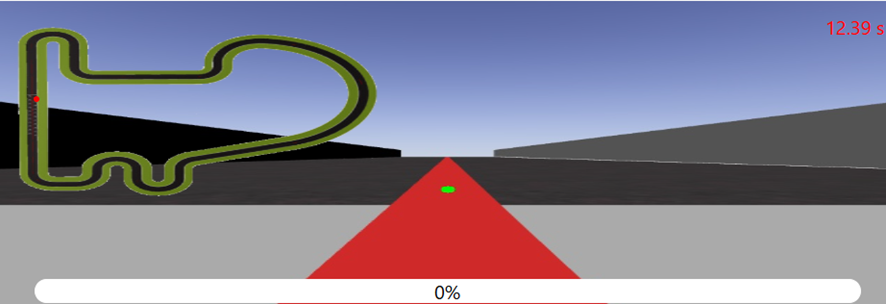
With this value, I proceeded to calculate the mask that will be used later as a reference for the control system. Although the value was obtained in RGB, it is preferable to use the HSV color space because it separates color information from illumination, allowing for a more stable detection under different lighting conditions.
To account for possible variations in the line’s tone, I defined a small range of ±10, which is then used to filter the pixels in the captured image to obtain the final mask.